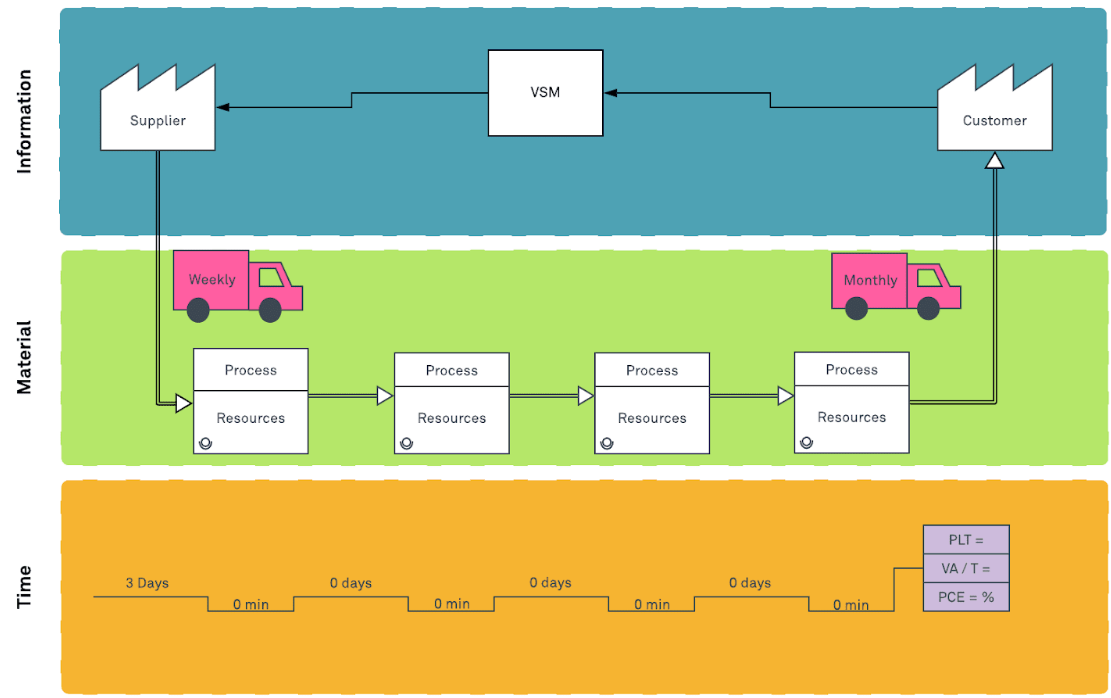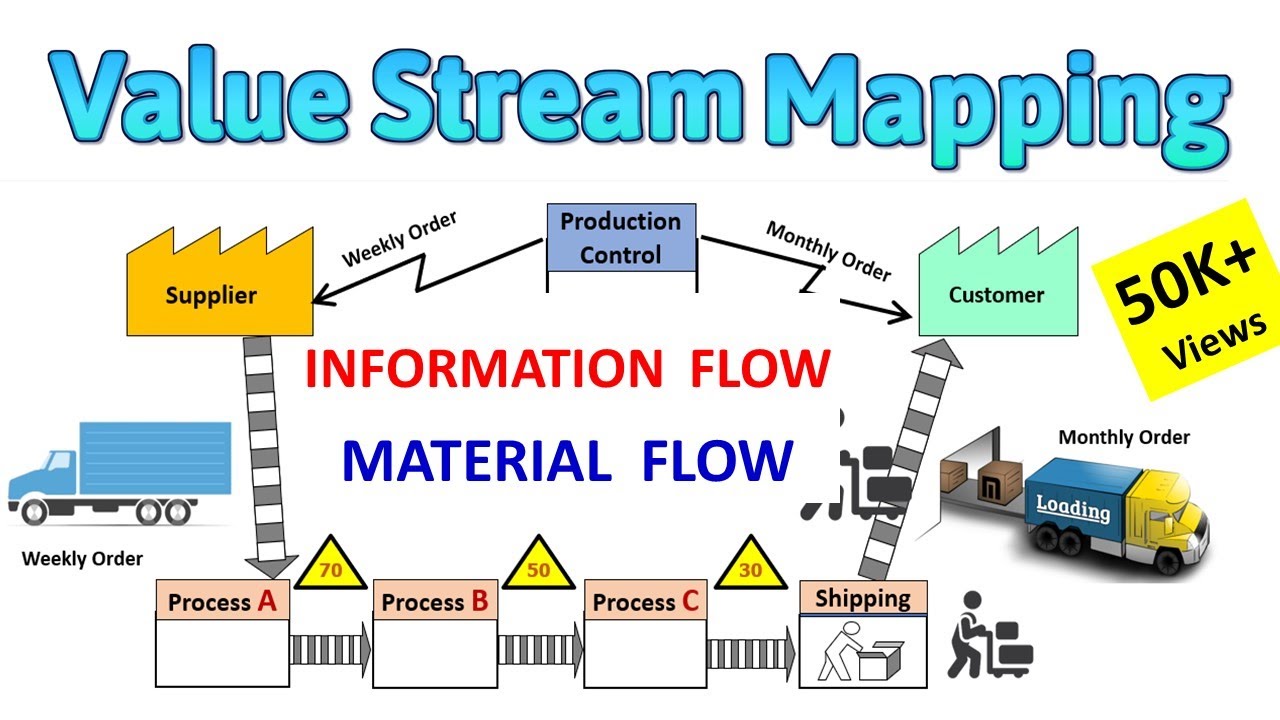
Value stream mapping is a powerful tool that can help organizations visualize the entire process of delivering a product or service. By mapping the value stream, businesses can identify waste, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement.
What is Value Stream Mapping?
A value stream map is a visual representation of all the steps involved in producing a product or service. It shows the flow of materials, information, and work from start to finish. By mapping the value stream, businesses can identify activities that add value to the customer and those that do not.
The Steps of Value Stream Mapping
The process of creating a value stream map involves the following steps:
- Define the scope: Determine the product or service that you want to map.
- Identify the process steps: Break down the process into individual steps.
- Gather data: Collect data on the time it takes to complete each step, the distance materials travel, and the amount of inventory.
- Create the map: Draw a diagram that shows the flow of materials and information.
- Identify waste: Use the map to identify waste, such as waiting time, transportation, and unnecessary movement.
- Develop improvement actions: Based on the identified waste, develop actions to eliminate or reduce it.
Types of Value Stream Maps
There are two main types of value stream maps:
- Current state map: This map shows the current process, including all the waste and inefficiencies.
- Future state map: This map shows the ideal process, with all waste eliminated.
Benefits of Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Improved understanding of the process: By creating a visual representation of the process, businesses can gain a better understanding of how it works.
- Identification of waste: Value stream mapping can help businesses identify waste that is hidden in their processes.
- Prioritization of improvement efforts: By focusing on the areas of the process that contribute the most to waste, businesses can prioritize their improvement efforts.
- Improved communication: Value stream maps can be used to communicate the process to employees and stakeholders.
- Reduced lead time: By eliminating waste and improving the flow of work, businesses can reduce lead times.
Examples of Waste in Value Stream Mapping
Some common types of waste that can be identified through value stream mapping include:
- Overproduction: Producing more than is needed.
- Waiting: Time spent waiting for materials, information, or equipment.
- Transportation: Moving materials or products unnecessarily.
- Inventory: Excess inventory that is not needed.
- Motion: Unnecessary movement of people or materials.
- Overprocessing: Performing more work than is necessary.
- Defects: Producing products or services that do not meet customer requirements.
Tips for Successful Value Stream Mapping
- Involve the right people: Make sure that the people who are involved in the process are involved in the mapping process.
- Use a simple format: Keep the map simple and easy to understand.
- Be specific: Use specific data to populate the map.
- Continuously update the map: As the process changes, update the map to reflect the new reality.
Value stream mapping is a powerful tool that can help businesses identify waste, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. By following the steps outlined above, businesses can create effective value stream maps and use them to drive continuous improvement.