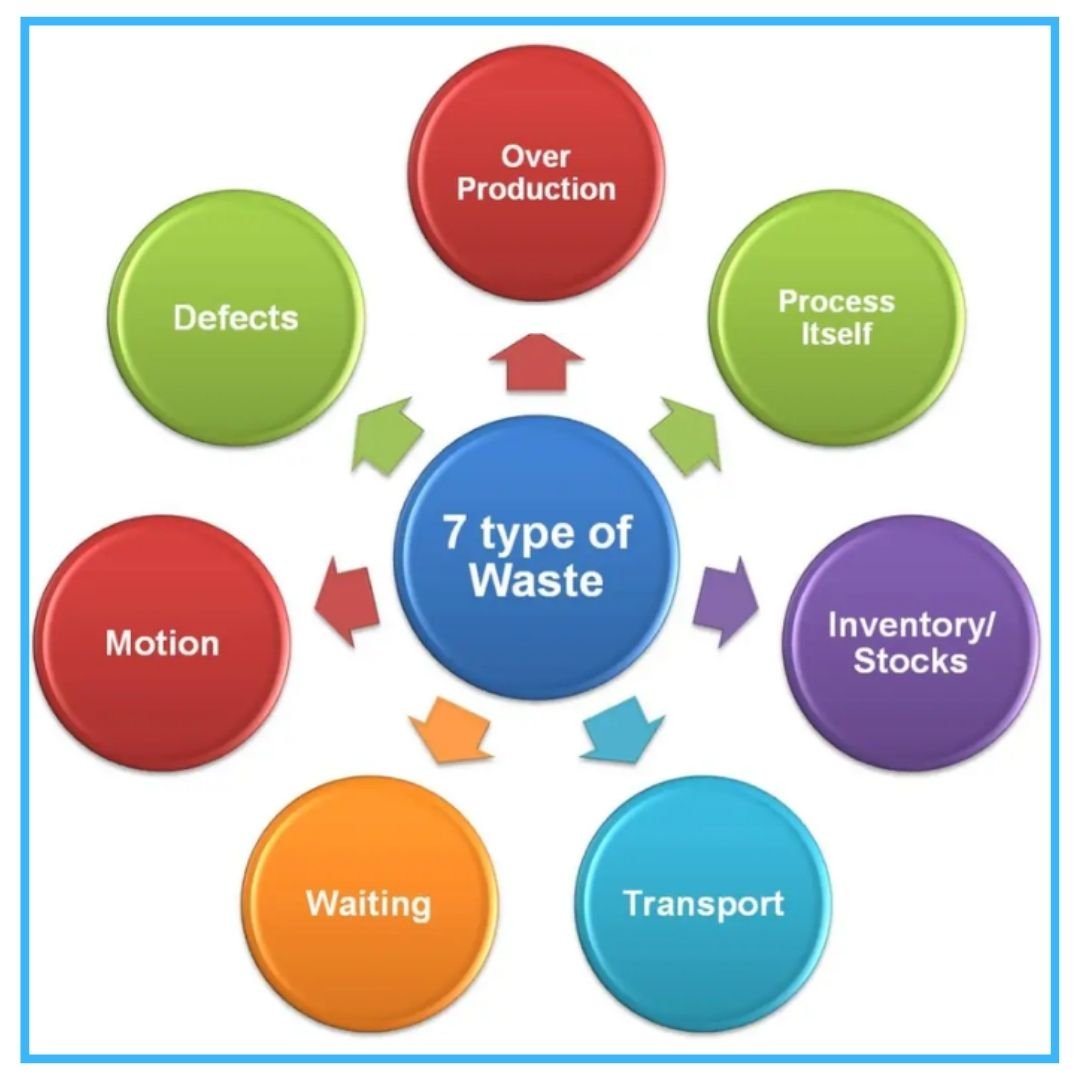
Lean manufacturing is a philosophy that focuses on identifying and eliminating waste in all areas of operations. There are seven types of waste that are commonly found in manufacturing processes:
- Overproduction: Producing more than is needed.
- Waiting: Time spent waiting for materials, information, or equipment.
- Transportation: Moving materials or products unnecessarily.
- Inventory: Excess inventory that is not needed.
- Motion: Unnecessary movement of people or materials.
- Overprocessing: Performing more work than is necessary.
- Defects: Producing products or services that do not meet customer requirements.
By identifying and eliminating these seven wastes, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality.
Overproduction
Overproduction occurs when businesses produce more than is needed. This can lead to excess inventory, which can tie up capital and increase the risk of obsolescence. To eliminate overproduction, businesses should focus on producing only what is needed, when it is needed.
Waiting
Waiting occurs when materials, information, or equipment are not available when they are needed. This can lead to delays in production and increased costs. To eliminate waiting, businesses should improve their scheduling and planning processes.
Transportation
Transportation occurs when materials or products are moved unnecessarily. This can lead to increased costs and damage to products. To eliminate transportation, businesses should reduce the distance that materials and products need to travel.
Inventory
Inventory occurs when businesses have more inventory than they need. This can tie up capital and increase the risk of obsolescence. To eliminate inventory, businesses should focus on producing only what is needed, when it is needed.
Motion
Motion occurs when people or materials move unnecessarily. This can lead to increased fatigue and reduced productivity. To eliminate motion, businesses should redesign their workspaces and processes to minimize unnecessary movement.
Overprocessing
Overprocessing occurs when businesses perform more work than is necessary to meet customer requirements. This can lead to increased costs and reduced quality. To eliminate overprocessing, businesses should identify and eliminate unnecessary steps in their processes.
Defects
Defects occur when products or services do not meet customer requirements. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction and increased costs. To eliminate defects, businesses should focus on preventing defects from occurring in the first place.
By identifying and eliminating these seven wastes, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality.